查询缓存和逆向工程
查询缓存
一级缓存
一级缓存 :同一个SqlSession对象
MyBatis默认开启一级缓存,如果用同样的SqlSession对象查询相同的数据,则只会在第一次 查询时 向数据库发送SQL语句,并将查询的结果 放入到SQLSESSION中(作为缓存在);
后续再次查询该同样的对象时,则直接从缓存中查询该对象即可(即省略了数据库的访问)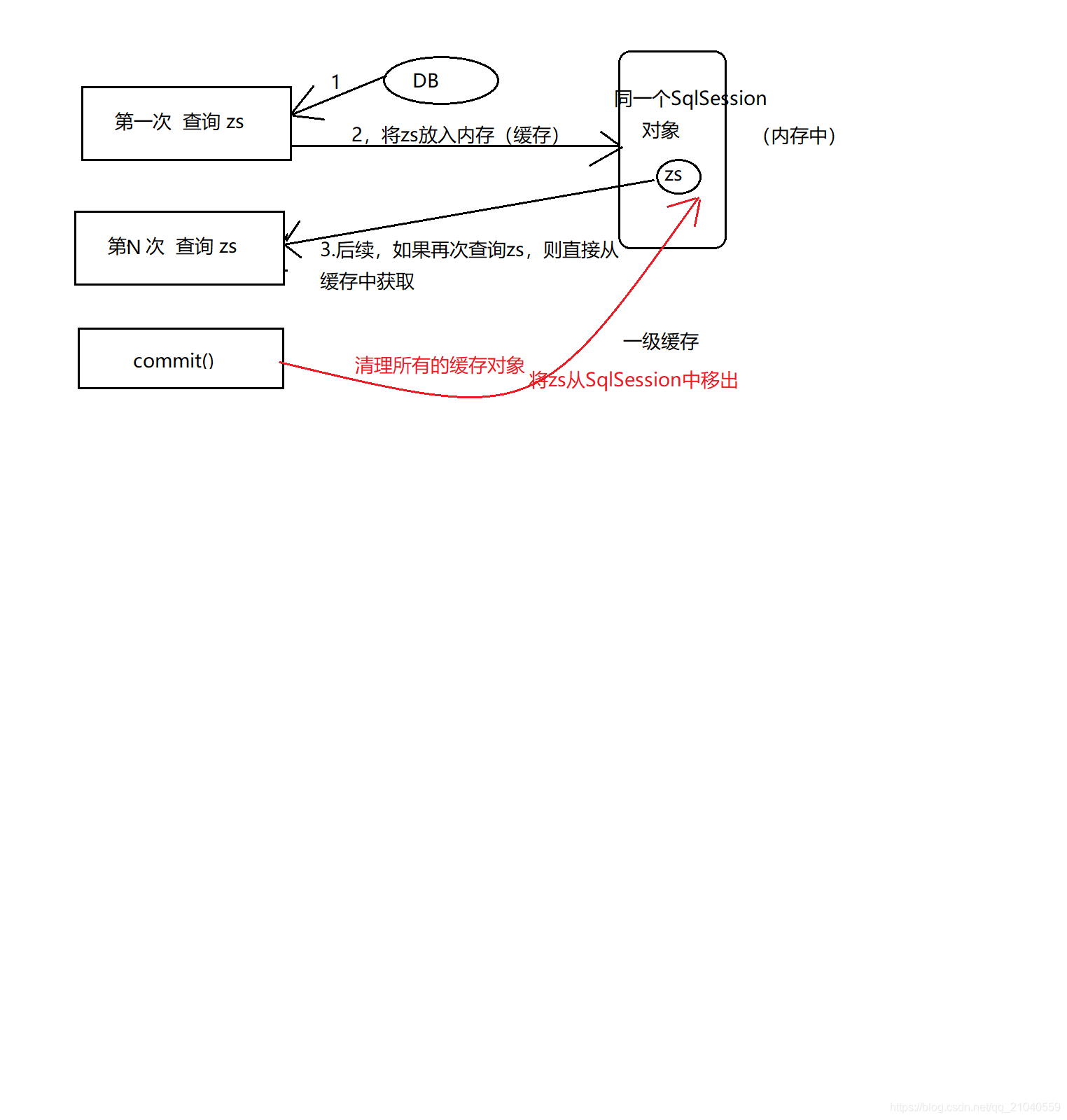
二级缓存
MyBatis默认情况没有开启二级缓存,需要手工打开。
a.conf.xml
<!-- 开启二级缓存 -->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
b.在具体的mapper.xml中声明开启(studentMapper.xml中)
<mapper namespace="org.lanqiao.mapper.StudentMapper">
<!-- 声明次namespace开启二级缓存 -->
<cache/>
根据异常提示:NotSerializableException可知,MyBatis的二级缓存 是将对象 放入硬盘文件中
序列化:内存->硬盘
反序列化:硬盘->内存
准备缓存的对象,必须实现了序列化接口 (如果开启的缓存Namespace=“org.lanqiao.mapper.StudentMapper”),可知序列化对象为Student,因此需要将Student序列化 (序列化Student类,以及Student的级联属性、和父类)
触发将对象写入二级缓存的时机:SqlSession对象的close()方法。
public static void queryStudentBystuno2() throws Exception {
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("config.xml");//把该配置文件变成对象
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sessionFactory.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student = mapper.queryStudentByStuno(2);
session.close();
SqlSession session2 = sessionFactory.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper2 = session2.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student2 = mapper2.queryStudentByStuno(2);
System.out.println(student.getStuNo()+","+student.getStuName());
System.out.println(student2.getStuNo()+","+student2.getStuName());
session2.close();
}
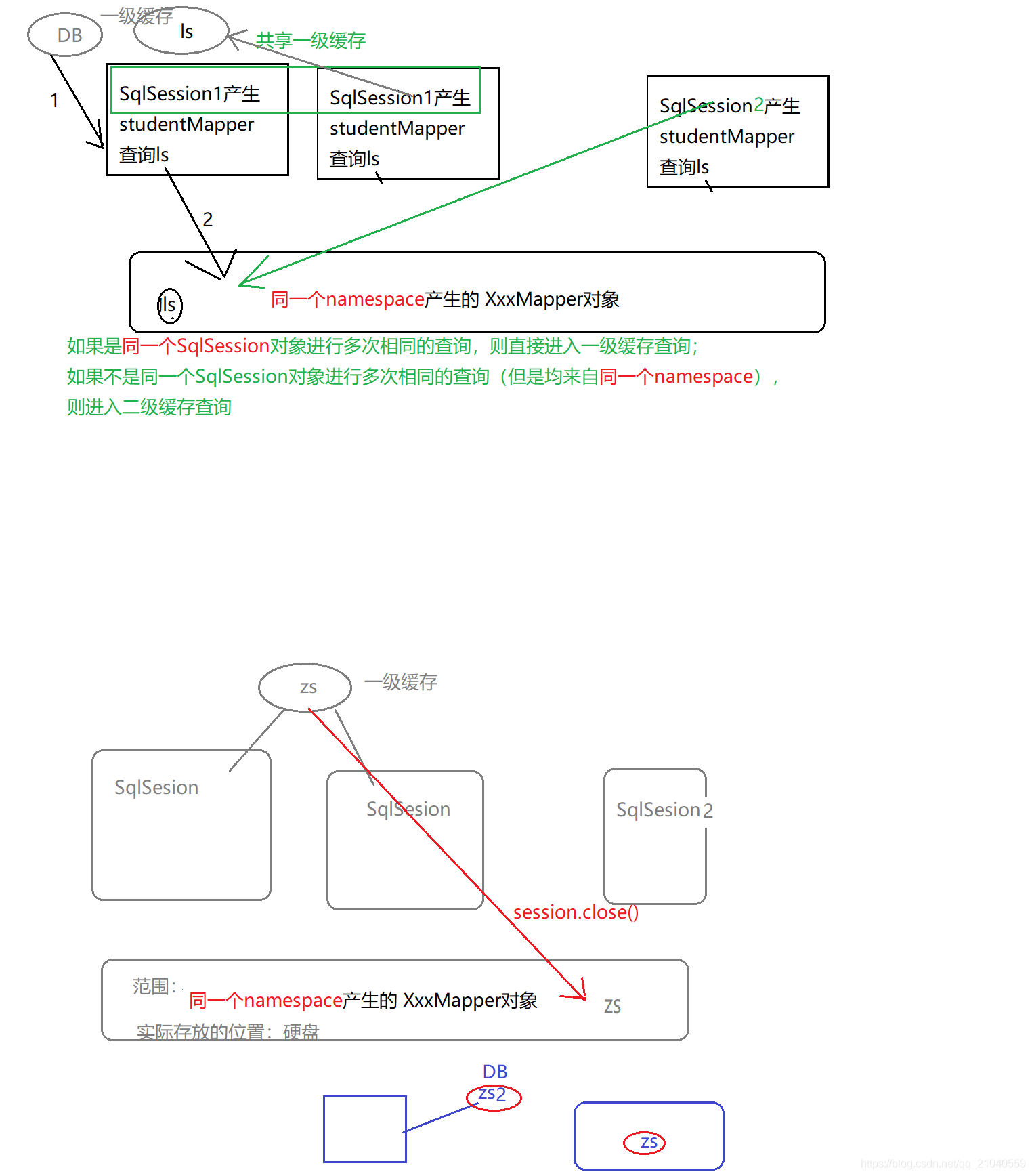
Mybatis自带二级缓存:【同一个namespace】生成的mapper对象
namespace的值 就是 接口的全类名(包名.类名), 通过接口可以产生代理对象(studentMapper对象)
-->namespace决定了studentMapper对象的产生
结论:只要产生的xxxMapper对象 来自于同一个namespace,则 这些对象 共享二级缓存。
注意:二级缓存 的范围是同一个namespace, 如果有多个xxMapper.xml的namespace值相同,则通过这些xxxMapper.xml产生的xxMapper对象仍然共享二级缓存。
命中率
Cache Hit Ratio [org.cduck.mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
Cache Hit Ratio [org.cduck.mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.5
第一次查询,二级缓存中没有该对象,所以第一次命中率为0,第二次再去查经过了缓存,所以能在二级缓存中查询到该对象。共查询两次,一次在缓存中查到,所以第二次的命中率为0.5。
禁用与清理
禁用 :select标签中useCache="false"
清理:a.与清理一级缓存的方法相同
commit(); (一般执行增删改时 会清理掉缓存;设计的原因 是为了防止脏数据)
在二级缓存中,commit()不能是查询自身的commit。
commit会清理一级和二级缓存;但是 清理二级缓存时,不能是查询自身的commit;
b. 在select标签中 增加属性 flushCache="true"
三方提供的二级缓存:
ehcache、memcache
要想整合三方提供的二级缓存 (或者自定义二级缓存),必须实现org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache接口,该接口的默认实现类是PerpetualCache
整合ehcache二级缓存:
a.
ehcache-core.jar
mybatis-Ehcache.jar
slf4j-api.jar
b.编写ehcache配置文件 Ehcache.xml
c.开启EhCache二级缓存
在xxxMapper.xml中开启
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache">
<!-- 通过property覆盖Ehcache.xml中的值 -->
<property name="maxElementsInMemory" value="2000"/>
<property name="maxElementsOnDisk" value="3000"/>
</cache>
逆向工程
表、类、接口、mapper.xml四者密切相关,因此 当知道一个的时候 其他三个应该可以自动生成。
表->其他三个
实现步骤:
a. mybatis-generator-core.jar、mybatis.jar、mysql.jar
b. 逆向工程的配置文件generator.xml
c. 执行(编写test类)
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.mybatis.generator.api.MyBatisGenerator;
import org.mybatis.generator.config.Configuration;
import org.mybatis.generator.config.xml.ConfigurationParser;
import org.mybatis.generator.exception.XMLParserException;
import org.mybatis.generator.internal.DefaultShellCallback;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception, XMLParserException {
File file=new File("src/generator.xml");//配置文件
List<String> warnings=new ArrayList<>();
ConfigurationParser cp=new ConfigurationParser(warnings);
Configuration configuration=cp.parseConfiguration(file);
DefaultShellCallback shellCallback=new DefaultShellCallback(true);
//逆向工程核心类
MyBatisGenerator generator =new MyBatisGenerator(configuration, shellCallback, warnings);
generator.generate(null);
}
}



