文章目录
模拟海量数据
通过 存储过程(无return)/存储函数(有return)来模拟。
create database testdata ;
use testdata
create table dept
(
dno int(5) primary key default 0,
dname varchar(20) not null default '',
loc varchar(30) default ''
)engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
create table emp
(
eid int(5) primary key,
ename varchar(20) not null default '',
job varchar(20) not null default '',
deptno int(5) not null default 0
)engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
通过存储函数 插入海量数据:
创建存储函数:
randstring(6) ->aXiayx 用于模拟员工名称
delimiter $
create function randstring(n int) returns varchar(255)
begin
declare all_str varchar(100) default 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ' ;
declare return_str varchar(255) default '' ;
declare i int default 0 ;
while i<n
do
set return_str = concat( return_str, substring(all_str, FLOOR(1+rand()*52) ,1) );
set i=i+1 ;
end while ;
return return_str;
end $
注意:
1、如果报错:You have an error in your SQL syntax,说明SQL语句语法有错,需要修改SQL语句;
2、 如果报错This function has none of DETERMINISTIC, NO SQL, or READS SQL DATA in its declaration and binary logging is enabled (you might want to use the less safe log_bin_trust_function_creators variable)
是因为 存储过程/存储函数在创建时 与之前的 开启慢查询日志冲突了
解决:
①临时解决( 开启log_bin_trust_function_creators )
show variables like '%log_bin_trust_function_creators%';
set global log_bin_trust_function_creators = 1;
②永久解决:
vi /etc/my.cnf
[mysqld]
log_bin_trust_function_creators = 1
产生随机整数:
create function ran_num() returns int(5)
begin
declare i int default 0;
set i =floor( rand()*100 ) ;
return i ;
end $
通过存储过程插入海量数据:emp表
create procedure insert_emp( in eid_start int(10),in data_times int(10))
begin
declare i int default 0;
set autocommit = 0 ;
repeat
insert into emp values(eid_start + i, randstring(5) ,'other' ,ran_num()) ;
set i=i+1 ;
until i=data_times
end repeat ;
commit ;
end $
通过存储过程插入海量数据:dept表
create procedure insert_dept(in dno_start int(10) ,in data_times int(10))
begin
declare i int default 0;
set autocommit = 0 ;
repeat
insert into dept values(dno_start+i ,randstring(6),randstring(8)) ;
set i=i+1 ;
until i=data_times
end repeat ;
commit ;
end$
插入数据:
delimiter ;
call insert_emp(1000,800000) ;
call insert_dept(10,30) ;

分析海量数据
(1)profiles
show profiles ; --默认关闭
show variables like '%profiling%';
set profiling = on ;
show profiles :会记录所有profiling打开之后的 全部SQL查询语句所花费的时间。缺点:不够精确,只能看到 总共消费的时间,不能看到各个硬件消费的时间(cpu io )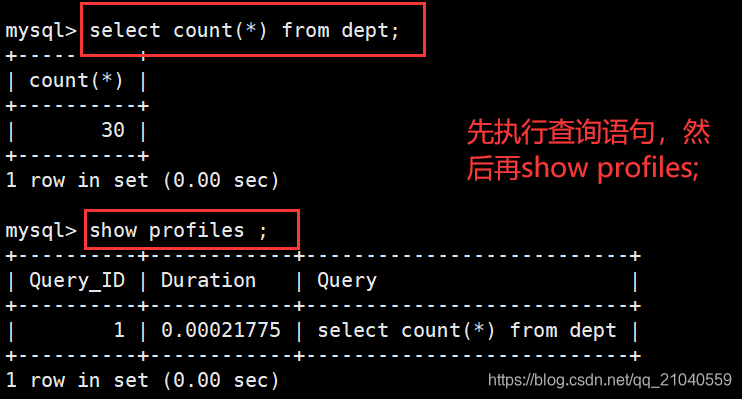
(2)–精确分析:sql诊断
show profile all for query 上一步查询的的Query_Id
show profile cpu,block io for query 上一步查询的的Query_Id

(3)全局查询日志 :记录开启之后的 全部SQL语句。
这次全局的记录操作 仅仅在调优、开发过程中打开即可,在最终的部署实施时 一定关闭
show variables like '%general_log%';--查看状态
--执行的所有SQL记录在表中
set global general_log = 1 ;--开启全局日志
set global log_output='table' ; --设置 将全部的SQL 记录在表中
--执行的所有SQL记录在文件中
set global log_output='file' ;
set global general_log = on ;
set global general_log_file='/tmp/general.log' ;
开启后,会记录所有SQL : 会被记录 mysql.general_log表中。
select * from mysql.general_log ;




