BlockingQueue 阻塞队列
阻塞队列
阻塞队列,顾名思义,首先它是一个队列,而一个阻塞队列在数据结构中所起的作用大致如下图所示: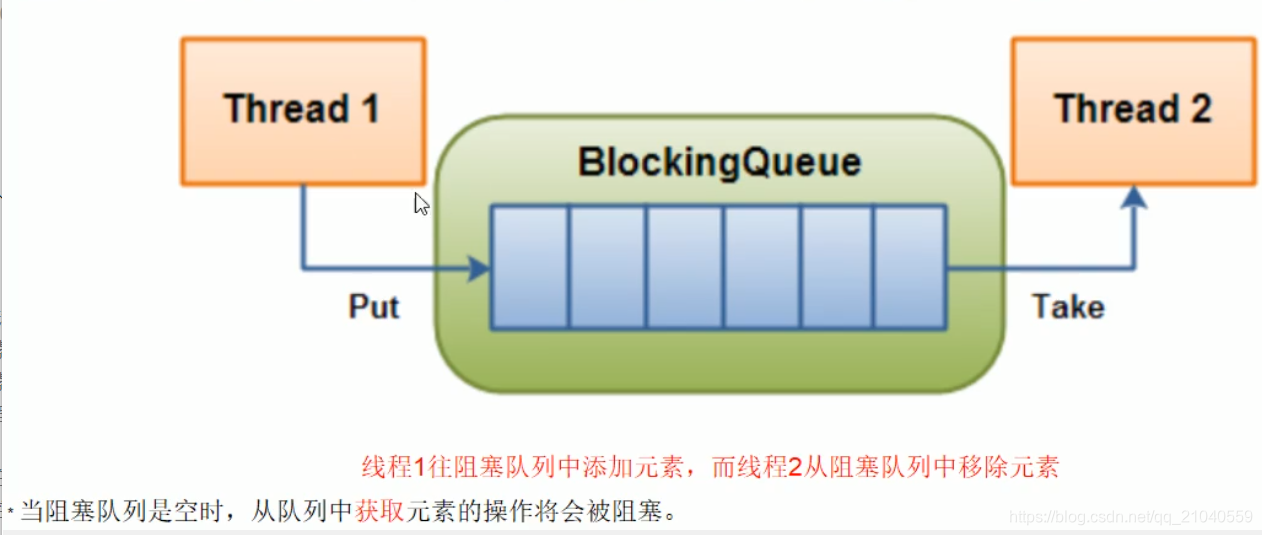
线程1往阻塞队列里添加元素,线程2从阻塞队列里移除元素
当队列是空的,从队列中获取元素的操作将会被阻塞。
当队列是满的,从队列中添加元素的操作将会被阻塞。
试图从空的队列中获取元素的线程将会被阻塞,直到其他线程往空的队列插入新的元素。
试图向已满的队列中添加新元素的线程将会被阻塞,直到其他线程从队列中移除一个或多个元素或者完全清空,使队列变得空闲起来并后续新增
阻塞队列的用处
在多线程领域:所谓阻塞,在某些情况下会挂起线程(即阻塞),一旦条件满足,被挂起的线程又会自动被唤起。
- 为什么需要BlockingQueue?
因为我们不需要关心什么时候需要阻塞线程,什么时候需要唤醒线程,因为这一切BlockingQueue都给你一手包办了,在concurrent包发布以前,在多线程环境下,我们每个程序员都必须去自己控制这些细节,尤其还要兼顾效率和线程安全,而这会给我们的程序带来不小的复杂度。
BlockingQueue的架构图
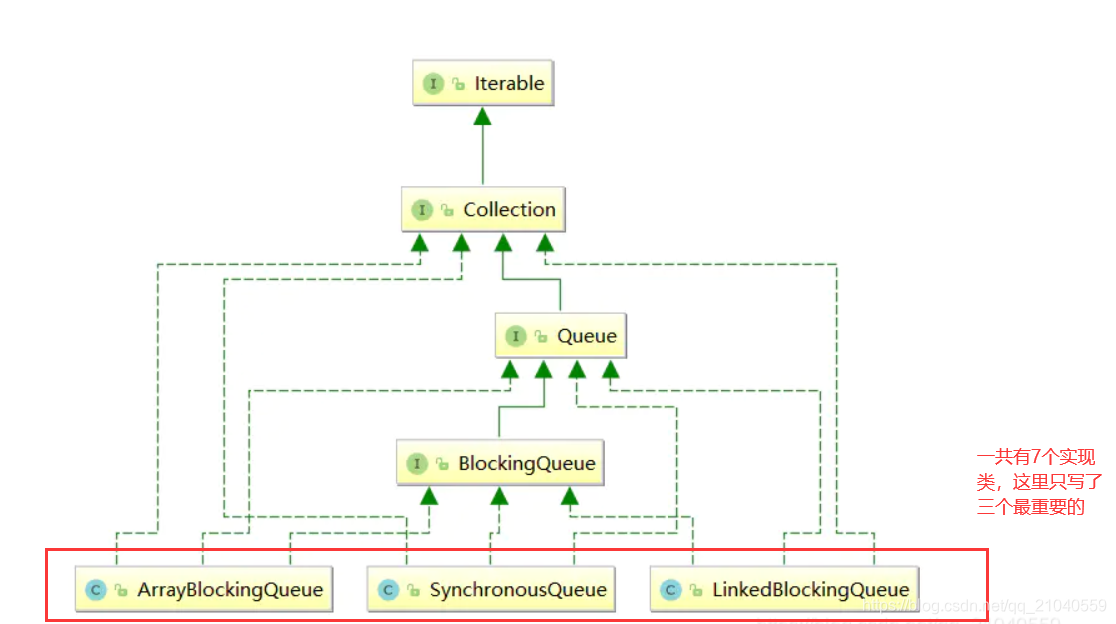
种类分析

BlockingQueue核心方法
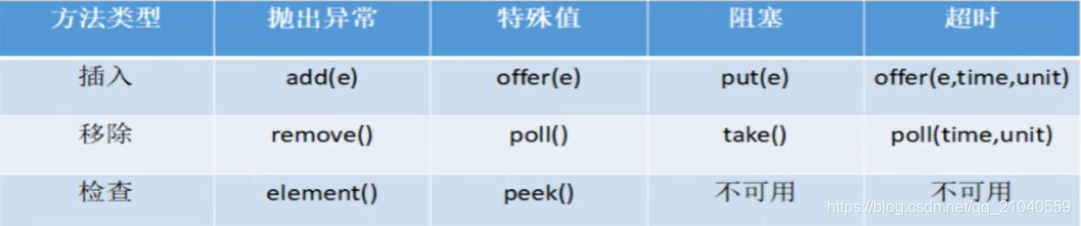
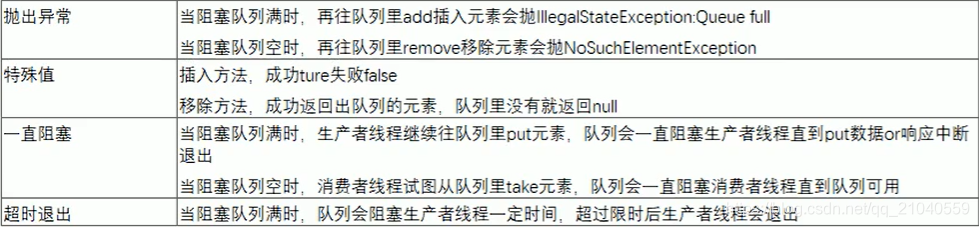
建议一组一组的配合着用,比如 插入是抛出异常组的,那么移除也用抛出异常组的
代码
package cduck.cn;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class BlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue=new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
/* System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("a"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("b"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("c"));*/
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("d")); 会出现异常队列已满
/* System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());*/
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove()); 会出现java.util.NoSuchElementException
/* System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c"));*/
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("e")); 会返回falseSystem.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("e",3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));//会在阻塞三秒后返回FALSE
/* System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());*/
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll()); 会返回null
/* blockingQueue.put("a");
blockingQueue.put("b");
blockingQueue.put("c");
添加成功不会有任何提示 只会显示正常退出
*/
/* System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());*/
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());会一直阻塞着进程 等待队列中加入可以让它拿的元素
}
}
再来单独看看SynchronousQueue
不存储元素的阻塞队列,也即单个元素的队列
public class SynchronousQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue blockingQueue = new SynchronousQueue();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t put 1.");
blockingQueue.put("1");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t put 2.");
blockingQueue.put("2");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t put 3.");
blockingQueue.put("3");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t take" + blockingQueue.take());
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t take" + blockingQueue.take());
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t take" + blockingQueue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "B").start();
}
}




