第四种模型< Routing >
Routing 之订阅模型-Direct(直连)
在Fanout模式中,一条消息,会被所有订阅的队列都消费。但是,在某些场景下,我们希望不同的消息被不同的队列消费。这时就要用到Direct类型的Exchange。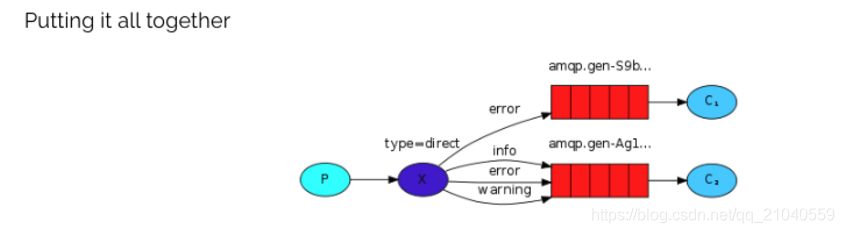
图解:
- P:生产者,向Exchange发送消息,发送消息时,会指定一个routing key。
- X:Exchange(交换机),接收生产者的消息,然后把消息递交给 与routing key完全匹配的队列
- C1:消费者,其所在队列指定了需要routing key 为 error 的消息
- C2:消费者,其所在队列指定了需要routing key 为 info、error、warning 的消息
在Direct模型下:
- 队列与交换机的绑定,不能是任意绑定了,而是要指定一个RoutingKey(路由key)
- 消息的发送方在 向 Exchange发送消息时,也必须指定消息的 RoutingKey。
- Exchange不再把消息交给每一个绑定的队列,而是根据消息的Routing Key进行判断,只有队列的Routingkey与消息的 Routing key完全一致,才会接收到消息
开发生产者
package cn.duck.Direct;
import cn.duck.Utils.RabbitMqUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Provider {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel=connection.createChannel();
// 通道声明交换机 参数一:交换机名称 参数二 交换机类型
channel.exchangeDeclare("logs_direct","direct");
// 发送消息
String routingKey="info";
channel.basicPublish("logs_direct",routingKey,null,("这是direct模型基于routingKey:"+routingKey+"\t发送的消息").getBytes());
RabbitMqUtils.close(channel,connection);
}
}
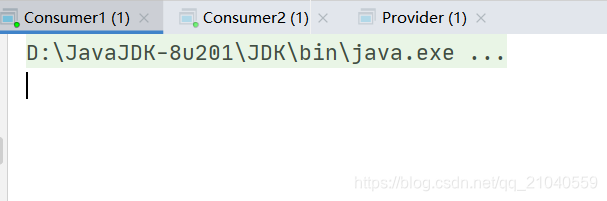
开发消费者1
package cn.duck.Direct;
import cn.duck.Utils.RabbitMqUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel=connection.createChannel();
// 通道声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare("logs_direct","direct");
// 创建一个临时队列
String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
// 用通道将交换机和临时队列绑定起来
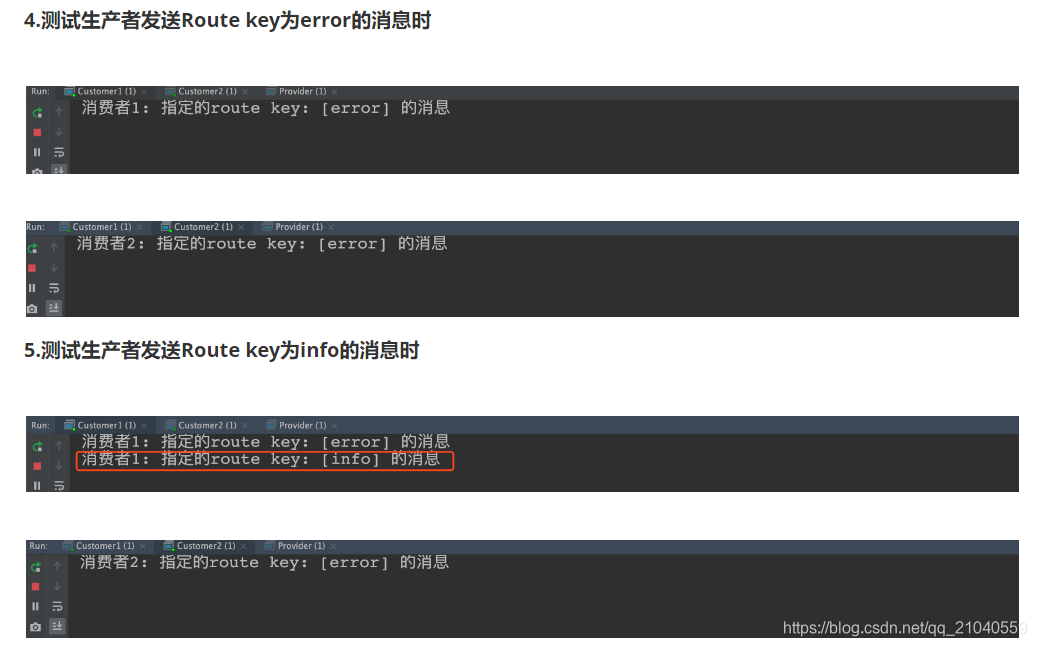
channel.queueBind(queue,"logs_direct","error");
// 获取生产者的信息
channel.basicConsume(queue,true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者1:"+new String(body));
}
});
}
}
开发消费者2
package cn.duck.Direct;
import cn.duck.Utils.RabbitMqUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel=connection.createChannel();
// 通道声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare("logs_direct","direct");
// 创建一个临时队列
String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
// 用通道将交换机和临时队列绑定起来
channel.queueBind(queue,"logs_direct","info");
channel.queueBind(queue,"logs_direct","error");
channel.queueBind(queue,"logs_direct","warning");
// 获取生产者的信息
channel.basicConsume(queue,true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者2:"+new String(body));
}
});
}
}
测试结果
Routing 之订阅模型-Topic
Topic类型的Exchange与Direct相比,都是可以根据RoutingKey把消息路由到不同的队列。只不过Topic类型Exchange可以让队列在绑定Routing key 的时候使用通配符!这种模型Routingkey 一般都是由一个或多个单词组成,多个单词之间以”.”分割,例如: item.insert
可以将Topic称为动态路由模型

通配符
* (star) can substitute for exactly one word. 匹配不多不少恰好1个词
# (hash) can substitute for zero or more words. 匹配一个或多个词
如:
audit.# 匹配audit.irs.corporate或者 audit.irs 等
audit.* 只能匹配 audit.irs
开发生产者
package cn.duck.Topic;
import cn.duck.Utils.RabbitMqUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Provider {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.exchangeDeclare("topics","topic");
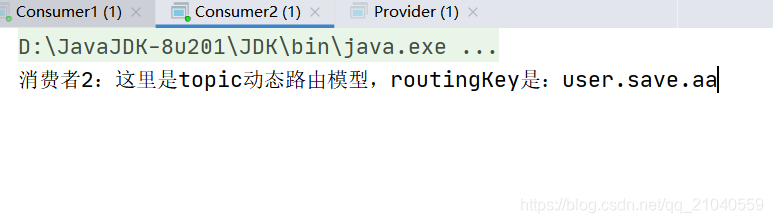
String routingKey="user.save.aa";
channel.basicPublish("topics",routingKey,null,("这里是topic动态路由模型,routingKey是:"+routingKey).getBytes());
RabbitMqUtils.close(channel,connection);
}
}
开发消费者1
package cn.duck.Topic;
import cn.duck.Utils.RabbitMqUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.exchangeDeclare("topics","topic");
// 临时队列
String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
channel.queueBind(queue,"topics","user.*");
channel.basicConsume(queue,true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者1:"+new String(body));
}
});
}
}
开发消费者2
package cn.duck.Topic;
import cn.duck.Utils.RabbitMqUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitMqUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.exchangeDeclare("topics","topic");
// 临时队列
String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
channel.queueBind(queue,"topics","user.#");
channel.basicConsume(queue,true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者2:"+new String(body));
}
});
}
}
测试结果